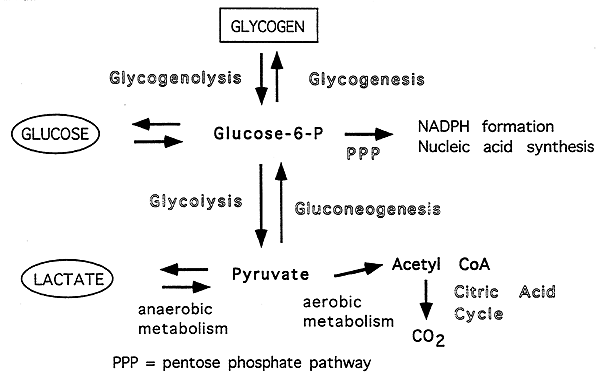
Glucose Transport:
1. You eat causing blood sugar to rise, this is known as the "Fed" state.
2. The liver signals the pancreas to release Insulin, a hormone responsible for utilizing blood glucose.
Insulin-Insensitive: uptake of glucose by the liver, brain and RBC is maximally active in the absence of insulin, insulin-insensitive. Since glucose reaches the liver before it signals the pancreas to release insulin it is important that the liver function independently of insulin. -----> prevents hyperglycemia.
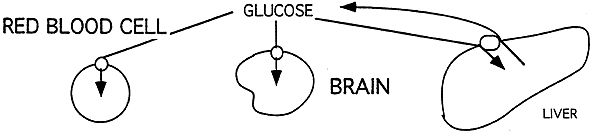
Insulin-Sensitive: associated with glucose promoting pancreatic release of insulin.
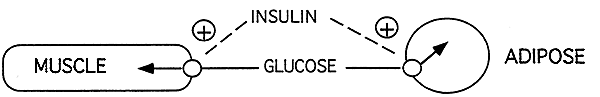
Pathways of the Carbohydrate System:
Glycolysis: splits glucose to pyruvate, which can be converted to lactate.
Gluconeogenesis: converts pyruvate to glucose.
Glycogenesis: synthesis of glycogen, carbohydrate fuel storage form.
Glycogenolysis: breakdown of glycogen.
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP): produces NADPH for cell biosynthesis.
Citric Acid Cycle: converts Acetyl CoA to CO2 and ENERGY
Note:
-lysis: splits
-genesis: creates