
Antioxidants, Cobalamin and Folic Acid
Biological Oxidants:
-Oxygen, essential for life is also potentially toxic.
-98% of oxygen used by cells is reduced to harmless ground state oxygen or water.
-However, a small fraction of the oxygen in cells is converted to Active Oxygen (AO) species which can damage DNA, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.
Free Radicals:
-An atom or group of atoms with an unpaired electron.
-Highly reactive.
-React with amino acids in proteins, lipids in membranes, bases in DNA.
-Products of these reactions generate other free radicals ---> chain reactions.
Active Oxygen Species (AO):

Singlet Oxygen:
Produced by UV Light

Though not really a "classic" free radical it is still very reactive. With two electrons singlet oxygen has an unstable conformation and is a great conributer to oxidative cellular damage.
Superoxide Radical Anion:

Though not a significant source of toxicity (short lived) it can be converted to hydrogen peroxide, peroxyl and hydroxyl radical.
Peroxyl Radical:

Hydroxyl Radical:

Produced from hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical is the most reactive AO species causing damage to all four classes of biomolecules.
Lipid Peroxyl Radical:

When a free radical (R. ) is formed it can react with a lipid to form a lipid radical, which in turn reacts with oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (LOO. ).
Antioxidant Vitamins: C, E and carotenoids
Vitamin C:

Ascorbic acid itself can be oxidized to form a free radical which can act directly with AO species then proceed through a series of reactions to oxalic acid.
Deficiencies: scurvy
Toxicities: increased oxalic acid production -------> kidney stones
RDA: 60 mg
Vitamin E: a-tocopherol (major species)

a-Tocopherol can transfer a hydrogen atom to lipid peroxyl radical forming a stable species which is ultimately recycled back to vitamin E.
Deficiencies: rare, anemia, neurologic disorders
Toxicities: interferes with vitamin K metabolism -----> blood coagulation disorders
RDA: 10 mg
Carotenoids: Vitamin A

Very effective quenchers of singlet oxygen (1O2).
Deficiencies: so far not demonstrated
Toxicities: harmless yellowing of palms and soles of feet
RDA: 1,000 mg
______________________________________________________________________________
Hematopoietic Vitamins
Hematopoietic refers to RBC division and more specifically a lack of the "hematopoietic" vitamins results in reduced RBC division and anemia.
Folic Acid:

Required: for the synthesis of pyrimidines in DNA ----> RBC division
Function: carrier of one carbon units (i.e. methyl transfer reactions)
Source: nearly all foods.
Deficiencies: rare, impaired DNA biosynthesis ----> reduced RBC division ----> anemia.
RDA: 200 mg
Supplements: prescribed during pregnancy to reduce the incidence of neural tube defects in newborns.
______________________________________________________________________________
Cobalamin (B12):
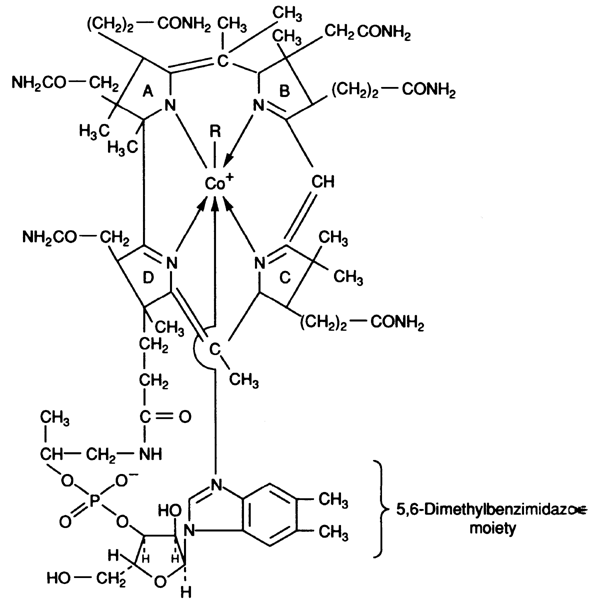
Required: for the synthesis of pyrimidines in DNA ----> RBC division.
Structure: complex molecule comprised of a metal (cobalt), a ring system and a nucleotide.
Function: carrier of one carbon units (i.e. methyl transfer reactions)
Source: must be synthesized by microorganisms, found in animal tissue or foods that have been bacterially fermented.
Deficiencies: rare, impaired DNA biosynthesis ----> reduced RBC division ----> anemia.
RDA: 2 mg
© Dr. Noel Sturm 2014