C A U T I O N
When preparing and handling solutions of potassium
permanganate, it is advisable to wear rubber gloves to avoid contact of the
solution with your skin; it will cause unsightly stains on your hands for
several days. If this oxidant comes in contact with the skin. wash the affected
area thoroughly with soap and warm water.
Residues of manganese dioxide on glassware can be
difficult to remove. Rinsing the glassware with sodium bisulfite solution will work.
Equation:
C6H5CH2CH3 + 4KMnO4 + 4HCl ---> C6H5CO2H + CO2 + 4MnO2 + 4KCl + 4H2O
Table of Physical Constants
| Compound | M.W. | Density | M.P. | B.P. |
| C6H5CH2CH3 | 106.0 | .o867 | -95 | 136 |
| C6H5COOH | 122.0 | 250 | ||
| KMnO4 | 158.0 |
Table of amounts of reactants used and of amounts of products theoretically possible
|
|
C6H5CH2CH3 |
KMnO4 |
6M HCl |
C6H5CO2H |
KCl |
CO2 |
H2O |
MnO2 |
|
|
MW |
106 |
158 |
36.5 |
122 |
84.5 |
44 |
18 |
87 |
|
|
Moles |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grams |
1.7 |
11.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Day 1
1. Bring your 250 mL round-bottom flask, wide-mouth funnel and cork ring over to the balance area.
2. Weigh out 11.2 gm. potassium permanganate into the flask.
3. Return to your desk, and rinse the funnel and neck of the flask (washbottle) until no purple color remains.
4. Add additional water to the flask so that it is no more than half-full, and clamp it above your hotplate.
5. Add your magnetic stirring bar to the flask and turn on the stirrer to a setting of 7 to 9. The contents of
your flask should be stirring vigorously - you should see a vortex at the center of the flask.
6. Add a plastic pipet full of 3 M Sodium Hydroxide, and 2 shots of ethylbenzene to the flask.
7. Place your greased reflux condenser in the flask.
8. Attach hoses to the condenser and gently run water through them. Water runs from bottom hose to top hose.
9. Turn on the heating portion of your hot plate/stirrer to a setting of “4". CAUTION: severe bumping occurs if heated too strongly.
10. Once a gentle reflux has been maintained for 15 mins., you are to finish your EAS product melting point
determination.
11. At the end of the 90 minute reflux period, turn off the heat, raise the flask an inch above the hot plate surface and continue stirring for an additional 5 minutes..
12. Remove the condenser and test the hot solution for unchanged permanganate by placing a drop of the reaction mixture on a piece of filter paper. If a purple ring appears around the brown spot of manganese dioxide, permanganate remains.
13. Destroy any excess permanganate by adding small amounts of solid sodium bisulfite to the mixture until the spot test is negative. Do not add a large excess of bisulfite.
14. Filter the hot mixture by vacuum filtration:
a. Connect a vacuum hose to the water/house vacuum.
b. Connect the other end of the vacuum hose to the side arm of your 500 mL filter flask.
c. Place your large Buchner Funnel assembly atop your filter flask.
d. Place a sheet of 7 cm. filter paper into your Buchner Funnel.
e. Wet the filter paper using the water in your wash bottle.
f. Turn on the house vacuum.
g. Mix a heaping spoonfull of filter aid with 50 mL of water and pour it onto the filter paper.
h. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the filter flask.
i. Remove the funnel and pour the contents of the filter flask down the sink.
j. Re-connect the funnel.
k. Reconnect the vacuum hose to the filter flask.
l. Pour your HOT reaction mixture onto the filter paper and filter the solution.
15. Rinse the reaction flask and filter cake with two 10-mL portions of hot water. Dispose of the filter cake into the recovery jar at the front of the room.
16. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the filter flask slowly, then turn off the water/vacuum.
17. The filtrate should be clear and colorless. If not, add additional sodium bisulfite noting any color/physical changes in the filtrate. Consult your instructor before proceeding.
18. Pour the filtrate into a 250 mL beaker, add a boiling stick and evaporate the filtrate to about 100 mL. Set your hotplate no higher than 8 . If the concentrate is turbid. filter it by gravity; the filtrate should be clear.
19. Cool the concentrate to room temperature, then acidify with 10 mL 6M hydrochloric acid.
20. Cool this mixture in an ice-water bath, and isolate the benzoic acid by vacuum filtration.
21. Wash the contents of the filter flask down the sink.
22. Recrystallize your crude product using between 25 and 50 mL of water as your solvent.
Place in your drawer on 11 cm filter paper supported by a big watch glass until next lab period. Make sure the solid is covered by another piece of 11 cm filter paper.
Day 2
Determine the yield, melting point and molecular weight of the pure benzoic acid obtained, and record them in the Results section of your lab report, complete with appropriate calculations. Identify the peaks on your IR and NMR.
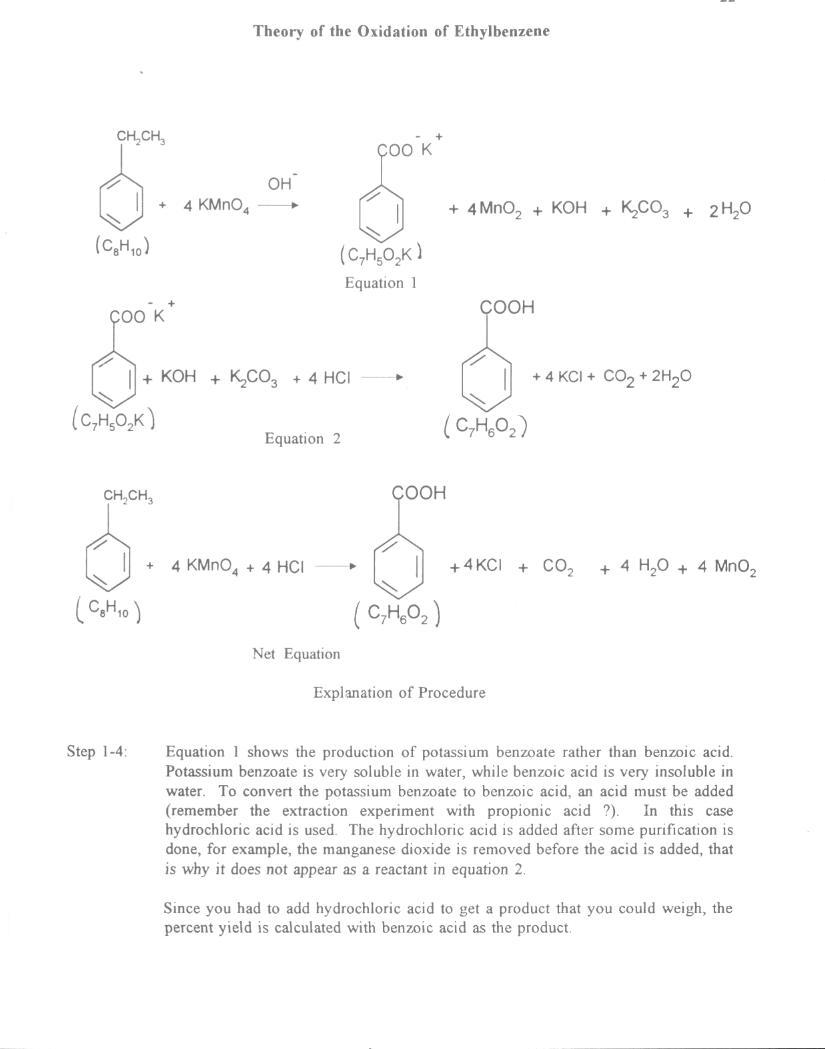
NMR for Ethylbenzene
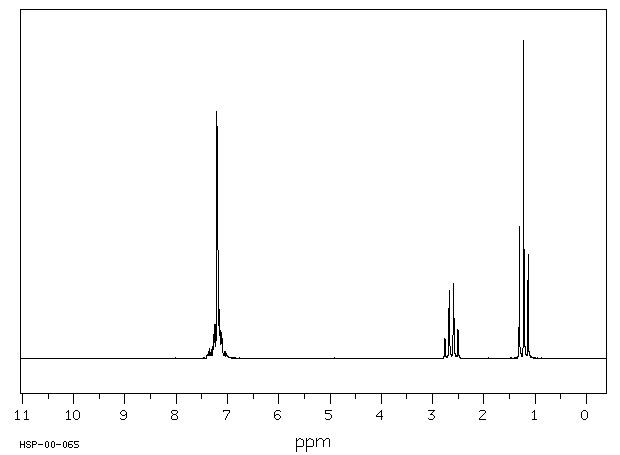
Assign. Shift(ppm)
A 1.22
B 2.63
C 7.0 to 7.45
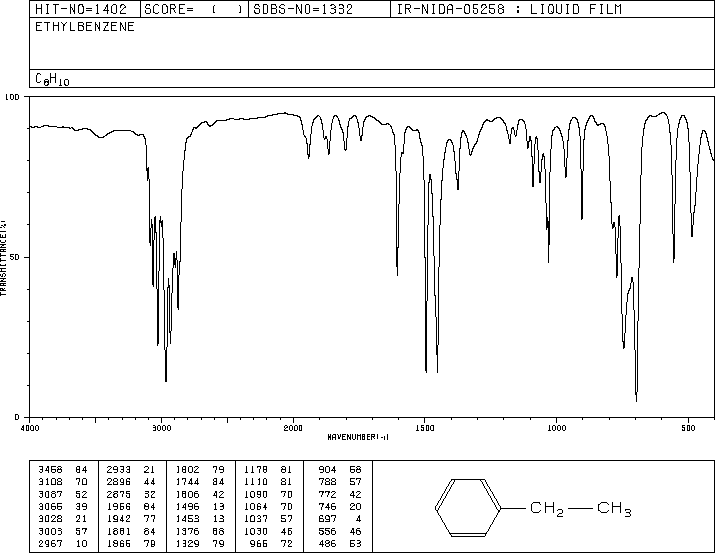
IR for Ethylbenzene
IR/NMR for Benzoic Acid
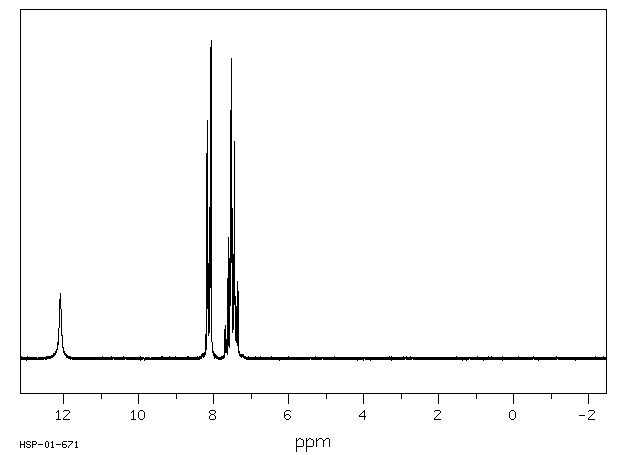
Assign. Shift(ppm)
A 12.09
B 8.12
C 7.62
D 7.45
IR/NMR for Benzoic Acid
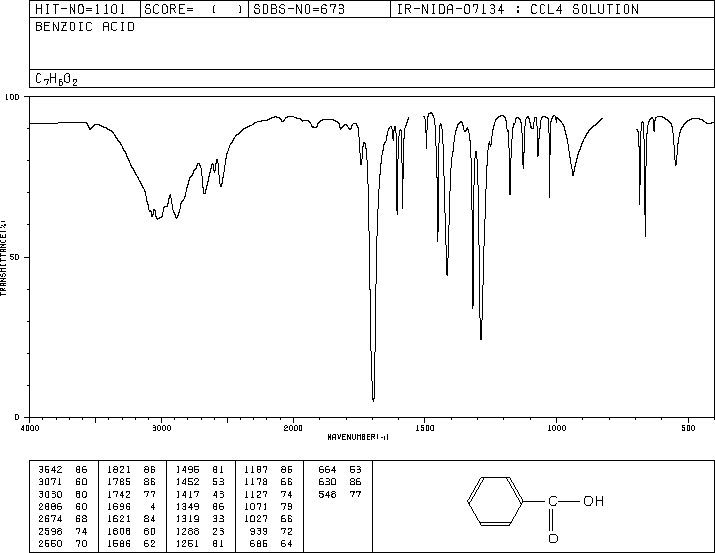
Molecular Weight Determination of Ethyl Benzene Product
1. Write a balanced equation for the titration
2. Accurately (to three decimal places) weigh 0.2 gm. of your dried product into a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask and dissolve it in 25-mL 95% Ethanol. Titrate the solution with 0.100 M NaOH to a faint pink end point, using 3 drops of phenolphthalein as your indicator. Calculate your equivalent weight using the following equation.
3. Calculate your molecular weight and compare it with that at the beginning of the experiment.
4. Calculate the % difference.
grams of acid
Molecular weight = -------------------------------------------------------------------
( volume of base consumed in liters ) x M
5. Record this calculation in the Results section of your lab report.
6. Any remaining benzoic acid should be returned to the recovery jar at the front of the lab.
Failure to properly dispose of your
product will result in a 2 point deduction from your lab score.