Steam Distillation
The purpose of this
experiment is to demonstrate the ability to distill an organic liquid at a
temperature considerably below that of the boiling point of the pure liquid.
Procedure
Construct the steam distillation apparatus as below, using a wide-stem funnel in your collection
vessel.
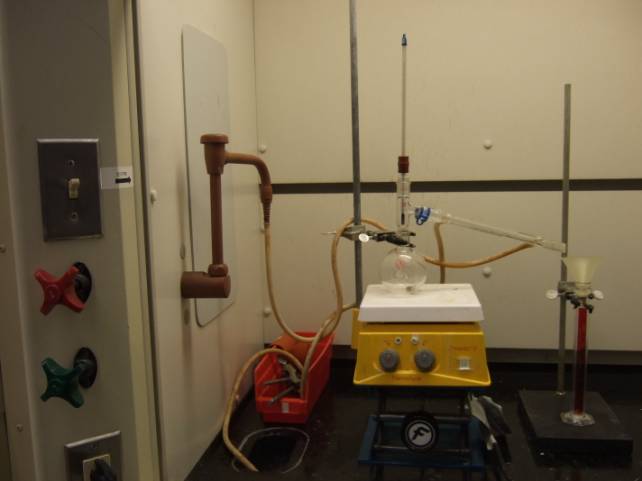

Add your pulp and water to the distillation pot UNTIL a bit OVER HALF FULL.
Add your magnetic stirring bar and start the mixture stirring. Heat the mixture to a boil,
initially heating at “7”.
Note: Attempt to control the rate of heating so that excessive foaming does not occur.
At the first drop of
distillate, record temperature and
volume of distillate collected. Repeat
this every four mL, until 28-32 mL of distillate has been collected.
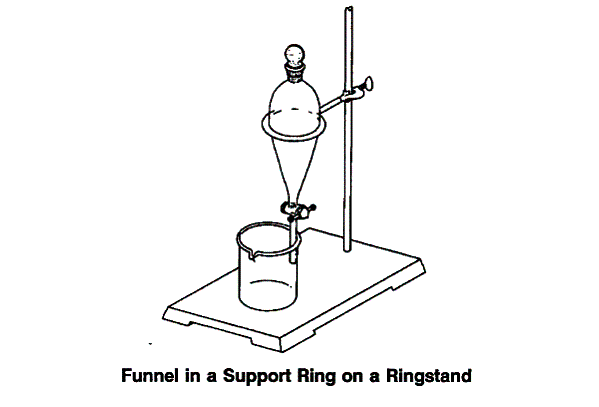
Stop the distillation. The distillate should have two layers. The top layer should be oil and
the bottom one should be aqueous. Transfer the distillate to a separatory funnel and allow the
mixture to stand for 5 - 10 minutes to allow complete separation. (See Figure above).
Drain off the aqueous layer.
Put the organic liquid (probably about 2 mL) in a clean, dry test tube and add a few granules
of anhydrous calcium chloride.
Measure the volume of the organic liquid (now dry).
Draw a Temperature vs Volume graph of your lab data in your lab
report.
Test for unsaturation (multiple bonds between two carbon atoms):
a) Place one drop of cyclohexane in a depression of a white spot plate and add 1 drop of KMnO4.
A purple color should be observed. There is no reaction. Stir the solution with a stirring rod and
spot the solution onto a piece of filter paper. A purple spot should be visible on the filter paper.
b) Place one drop of cyclohexene in a depression of a white spot plate and add 1 drop of KMnO4.
A red-brown color should form. Stir the solution with a stirring rod and spot the solution onto a
piece of filter paper. A brown spot should be visible on the filter paper.
c) Place one drop of your distilled oil in another depression of a white spot plate, and add 1 drop
KMnO4. red-brown color should form. Stir the solution with a stirring rod and spot the solution
onto a piece of filter paper. A brown spot should be visible on the filter paper.
Turn in your product in an appropriately labeled narrow mouth bottle.
==============================================
Disposal
of Spent Orange Peel
Pour the contents of your round-bottom flask into the large Buchner funnel set up on your
lab bench.
==============================================